Location, Mining Sites
PASTO GRANDE GROUP is a consortium formed by the companies DANPHIX from Peru and COPPERTAC, operating in southern Peru—Department of Puno. This region has favorable geological environments associated with lithium mineralization.
Southern Peru is part of the “Lithium Triangle” alongside Argentina and Chile, home to the world’s largest lithium reserves.
Our research confirms that this lithium-rich region extends into Peru, making it part of what is now known as the “Lithium Quadrangle.”
This geological formation resulted from volcanic activity, magma ascension, and fissures along the Central Andes Mountain Range, leading to the creation of an ancient sea known as El Gran Villiviam. Over time, this sea formed numerous endorheic basins, making it one of the largest lithium reserve areas on the planet.
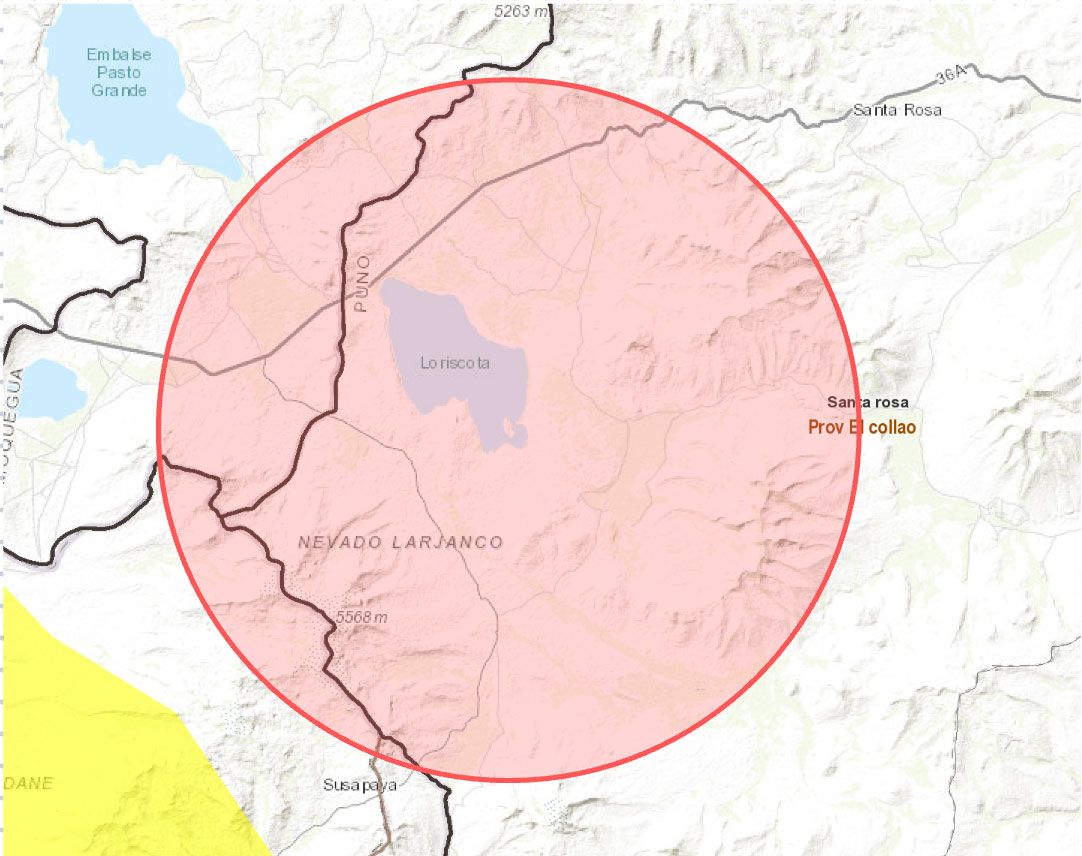
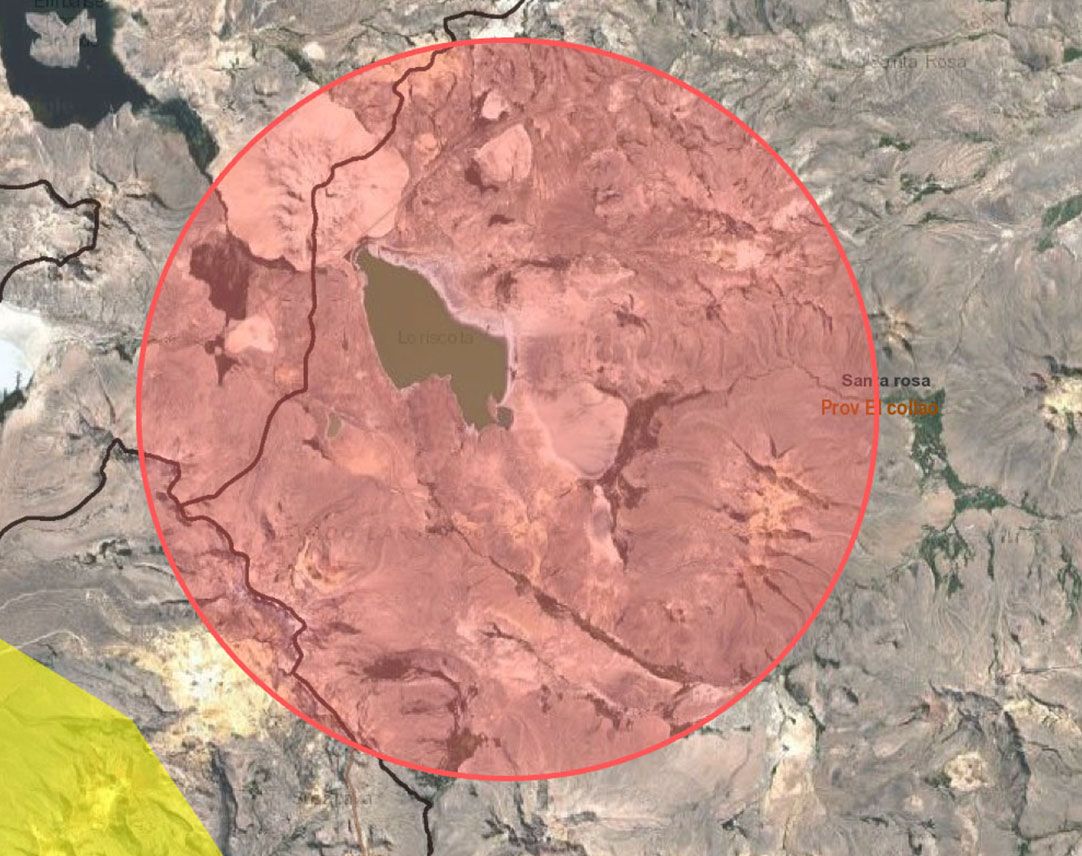
Our strategic location near ancient lakebeds, such as Laguna de Loriscota, has allowed us to conduct extensive surface exploration over 21,300 hectares of mining claims.
These areas meet the morpho-geological conditions necessary for the formation of large lithium deposits.

The Pasto Grande Lithium Consortium project is located in the province of El Collao, 54 km from the city of Puno, in Mazo Cruz – Santa Rosa District (Pasto Grande and Punta Perdida communities) in southern Peru.
The project focuses on salar deposits, which contain lithium alongside other valuable minerals such as potassium, boron, bromine, iodine, magnesium, and sodium carbonate. Lithium is found in salt flats (salares) associated with borates in arid volcanic regions, including the area currently under study.
The materials and minerals in the ancient Laguna de Loriscota were deposited in a glacial valley covered mostly by fluvioglacial material and sodium sulfate crusts. Volcanic pyroclastic rocks and lava flows from the Barroso volcanic formation are exposed on both sides of the valley.
Lithium-rich brines originate from hot springs, which contain lithium due to geothermal activity.
Exploration Area: Laguna de Loriscota
• Estimated lithium resources: 36 million metric tons
• Mining Concessions: 22 total covering 21,300 hectares
• Strategically located within the “Metallogenic Belt”, home to major lithium projects
Location:
The district of Santa Rosa is located in the southern part of the province of El Collao, in the department of Puno, within the southern Peruvian highlands.
Boundaries:
• North: Ilave district, province of El Collao, department of Puno.
• Southeast: Province of Candarave, department of Tacna.
• East: Province of Chucuito, department of Puno.
• West: Province of Mariscal Nieto, department of Moquegua.
Area and Population
The district covers an area of 2,524 km² and has an average altitude of 3,960 meters above sea level. According to the 2007 Population and Housing Census, the district had a population of 6,663 inhabitants, with a population density of 2.6 inhabitants per km². The 2017 Census recorded a population of 3,529 inhabitants, with a density of 1.4 inhabitants per km². Previously, a 2000 INEI study projected the district’s population at 10,479 inhabitants.
Climate
The climate is cold, with temperatures varying between 22°C (72°F) during the day and 0°C (32°F) at night.
Capital
Santa Rosa is one of five districts that make up the province of El Collao, department of Puno. It was officially established by law on February 5, 1854. Its capital is the town of Mazocruz, located at kilometer 220 on the Moquegua – Mazocruz – Desaguadero highway, which also connects to the cities of Tacna and Puno.
Access Routes
The strategic location near ports enhances ease of extraction and transportation, making the project highly competitive.
By Land
Route Distance Travel Time Road Type
Lima > Juliaca | 1,278 km | 20h 34m | Paved
Juliaca > Puno | 43.2 km | 51 min | Paved
Puno > Ilave | 54.7 km | 1h | Paved
Ilave > Mazocruz | 86.3 km | 1h 42m | Paved
Mazocruz > Laguna Loriscota | 43 km | 45 min | Paved
By Air
Route Flight Duration
Lima – Juliaca | 1h 25 min
By Sea
Ilo Port The Ilo Port Terminal, located 93 km from Moquegua and about 270 km from the concession areas, serves as an important point of access. The trip from Moquegua to Ilo takes approximately 1 hour and 20 minutes. The terminal features a multipurpose dock for deep-draft vessels, primarily used for exporting iron ore. Wheat is the main imported product. Another relevant reference point is Desaguadero, located 90 km from Mazocruz.
Economic Activities
Commerce
In key towns such as Mazocruz and Santa Rosa, small businesses and street vendors operate. Weekly Saturday markets in Mazocruz bring together traders and buyers to exchange products such as clothing, food, llama leather, and alpaca meat.
Passenger Transport
The district capital has a transportation agency that connects with routes to Moquegua, Tacna, and Puno. Some informal vehicles also transport passengers to Desaguadero.
Telecommunications
Mobile phone service is provided by Bitel, primarily available in Mazocruz. Some rural communities, such as Cuipa-Cuipa and Punta Perdida, rely on satellite radio communication.
Lodging and Dining
Mazocruz has two accommodations for visitors and a few small restaurants that serve local cuisine.
Financial Services
There are no banking services in the district; residents must travel to Moquegua for financial transactions.
Construction
Building activities, including housing and infrastructure, are mainly concentrated in Mazocruz.
Industry
There is no industrial activity in the district.
Mining
Currently, there active mining operation in Santa Rosa.
Agriculture
There are no agricultural activities in the study area.